In the quest for optimal health and well-being, the concept of personalized nutrition is gaining unprecedented attention. The idea is simple yet profound: tailor dietary recommendations based on individual genetic and metabolic profiles. This approach, supported by advancements in genomics and biotechnology, promises to revolutionize how we think about and manage our diets.
Understanding Personalized Nutrition
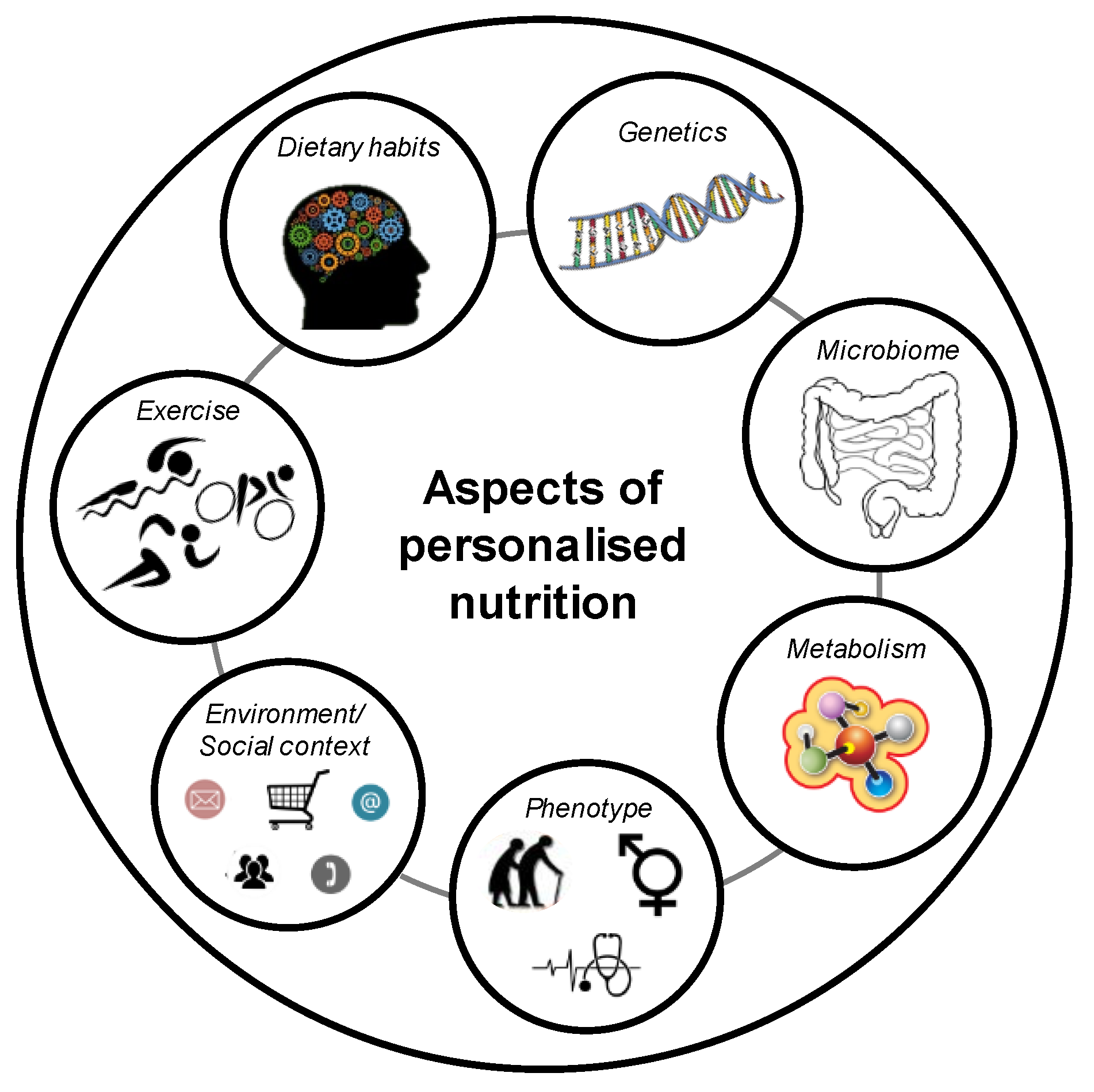
Personalized nutrition is a dietary approach that takes into account an individual's unique genetic makeup, metabolic rate, and lifestyle factors to create a customized diet plan. Unlike one-size-fits-all dietary guidelines, personalized nutrition aims to optimize health outcomes by considering the biological variations between individuals.
The Role of Genomics in Personalized Nutrition
Genomics—the study of genes and their functions—plays a pivotal role in personalized nutrition. Here's how:
Genetic Variants and Nutrient Metabolism: Genetic variants can influence how individuals metabolize different nutrients. For instance, variations in genes related to lactose intolerance can determine whether someone can digest dairy products efficiently. Similarly, certain genetic markers are associated with how well an individual absorbs and utilizes vitamins and minerals.
Predicting Nutritional Needs: By analyzing specific genetic markers, scientists can predict an individual's need for various nutrients. For example, some people may require higher levels of antioxidants due to genetic predispositions that make them more susceptible to oxidative stress.
Tailoring Dietary Recommendations: Genetic information can be used to provide tailored dietary recommendations. If a person's genetic profile suggests a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, a nutritionist might recommend a diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which can help reduce heart disease risk.
Metabolic Profiling and Its Impact on Nutrition
Metabolic profiling involves analyzing an individual’s metabolic responses to different foods and nutrients. This can provide insights into how different diets might affect one's health. Here's how it complements genetic insights:
Personalized Metabolic Data: Metabolic profiling can reveal how an individual's body processes various nutrients. For example, it can show how well they metabolize carbohydrates, proteins, or fats, helping to refine dietary recommendations further.
Understanding Food Sensitivities: Metabolic profiling can identify food sensitivities or intolerances that may not be immediately apparent. This information allows for more precise dietary adjustments to avoid adverse effects.
Optimizing Energy Levels: By understanding how one's metabolism responds to different types of foods, personalized nutrition can help optimize energy levels, enhance physical performance, and improve overall well-being.
The Process of Personalizing Nutrition
Genetic Testing: To start, individuals undergo genetic testing to identify specific genetic markers related to nutrition and metabolism. This often involves a simple saliva or blood test.
Analysis and Interpretation: The collected genetic data is analyzed to identify relevant markers that influence nutrient metabolism and health risks. Nutritionists or dietitians then interpret these results in the context of an individual's overall health.
Customized Diet Plan: Based on the genetic and metabolic information, a personalized diet plan is created. This plan includes recommendations on what foods to eat, avoid, or limit, as well as suggested portions and meal timings.
Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustment: Personalized nutrition is an ongoing process. Regular follow-ups and adjustments ensure that the diet plan continues to meet the individual’s evolving needs and goals.
The Benefits of Personalized Nutrition
Improved Health Outcomes: Tailoring diets based on genetic and metabolic profiles can lead to better health outcomes, including reduced risk of chronic diseases and improved management of existing conditions.
Enhanced Wellness: Personalized nutrition helps individuals achieve optimal wellness by aligning their diets with their unique biological needs, leading to increased energy levels, better mood, and overall improved quality of life.
Scientific Foundation: Unlike generic dietary recommendations, personalized nutrition is grounded in scientific research and data, providing more accurate and effective dietary advice.
Challenges and Considerations
While personalized nutrition offers promising benefits, there are challenges to consider:
Cost and Accessibility: Genetic testing and personalized nutrition consultations can be expensive and may not be accessible to everyone.
Privacy and Data Security: Genetic data is sensitive information. Ensuring its privacy and security is crucial.
Interpreting Results: The science of genomics and metabolism is complex, and accurate interpretation requires expertise.
Conclusion
Personalized nutrition, driven by genomic insights and metabolic profiling, represents a significant advancement in dietary science. By understanding and addressing individual genetic and metabolic differences, this approach holds the potential to transform health and wellness, providing tailored solutions that are far more effective than traditional dietary guidelines. As technology and research continue to evolve, personalized nutrition is set to become an integral part of our journey toward optimal health.
Embrace the future of nutrition—where your DNA informs your diet and your health thrives as a result.
0 Comments